IRIS: Enhancing the Security of IoT Devices Using Internal IR-Based Sensors
Authors: Amit Kama , Yarin Kalfon , Yossi Oren
Appeared in: Elsevier Internet of Things Journal, Volume 34, November 2025, 101787
Abstract
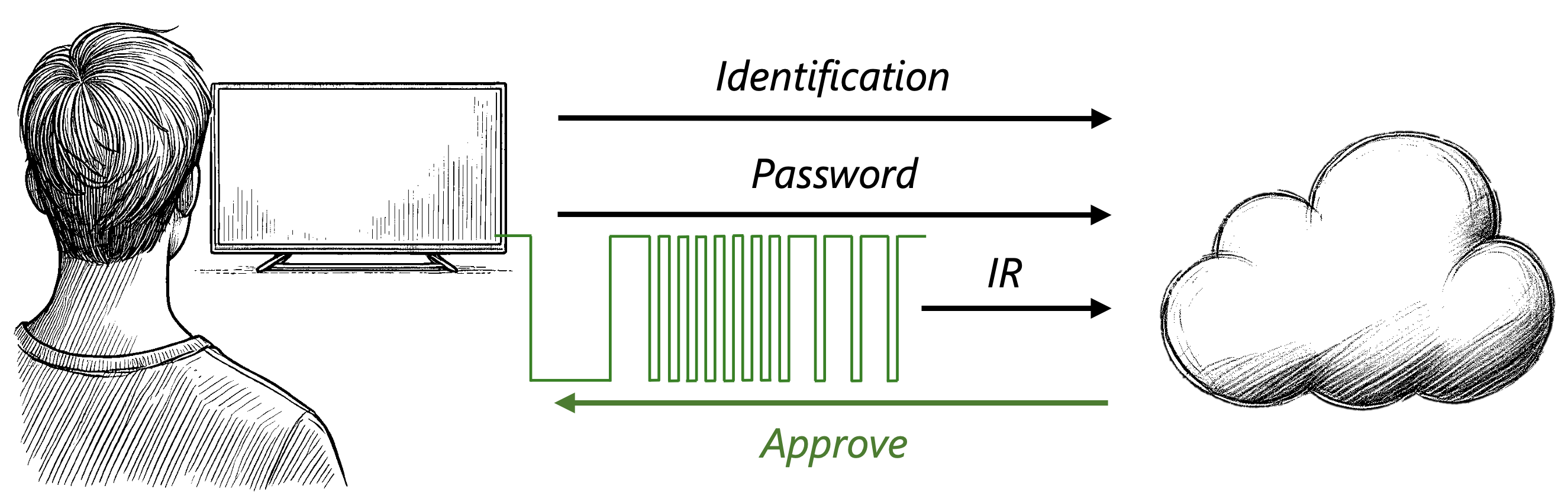
Authentication in Internet of Things (IoT) environments faces significant challenges due to the devices’ limited security capabilities and operational constraints, such as reduced computational power and energy. The unsecured and diverse settings in which these devices operate further complicate the implementation of traditional authentication protocols. While some work has explored leveraging intrinsic variations in Static Random-Access Memory (SRAM) characteristics for authentication, relatively little attention has been given to authentication approaches based on other sensors. In this work, we survey sensors commonly found in IoT devices and assess their suitability for authentication purposes. We identify the infrared (IR) receiver as a promising candidate for authentication, and demonstrate a practical method for using the inherent physical variations in these sensors to authenticate IoT devices. Our results demonstrate that IR receivers can authenticate IoT devices with an average accuracy of 0.9855, with a standard deviation of 0.014, above a base rate of 0.05. Motivated by these findings, we developed IRIS, a novel IR-based Identification System, and made an open-source artifact repository available to support further research. We also demonstrate the robustness of our proposed method under various constraints, such as shorter trace lengths, reduced sampling frequencies, relying solely on the receiver’s data, and authenticating with a TV remote control. Our findings suggest that low-cost sensors like IR receivers can significantly enhance IoT devices security without increasing their cost.